An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common type of electric motor operates by interacting between a wire winding and a magnetic field, resulting in force in the form of torque. The motor can be either permanent or reversible, and the latter type is usually the most popular and cost-effective of the two. Listed below are some examples of common uses of electric motors. But what are the disadvantages of electric motors?
An AC motor works by creating a magnetic field within the ac case. Three different electrical phases are introduced through terminals to energize each field pole. As the current increases, the magnetic field increases, decreasing the other phase. The resulting magnetic field fluctuates between the three poles and causes the rotor to rotate. This motion is called induction. The AC motor is a popular choice for home use because it is inexpensive and easy to build.
If you need a powerful electric motor, you need one with a large size and extensive copper windings. Rebuilding a large industrial motor is much more cost-effective than purchasing a new one. Once you've identified the type of motor you need, you can match it with the right motor. A good way to determine which one to purchase is by consulting the manufacturer's part number and physical dimensions. It's also useful to check the type of enclosure. This will tell you whether you need an enclosure for it, or whether it's a dangerous location.
An electric motor's synchronous speed is determined by the frequency of its power supply and the number of field coils. A 60-Hz supply is common in the United States. The synchronous speed of an electric motor is 3.600 rpm. Further reductions in the field current result in a higher speed and lower torque. Further reductions in the field current are called weak field operation. So the higher the speed, the faster the motor will spin.
Electric motors can vary in size and power, from a fraction of a watt to a multikilowatt device. The smallest electric motors operate computer disk drives and power windows and windshield wipers. The medium-sized ones are used in kitchen appliances like blenders and electric shavers. Large electric motors are used in industrial settings like elevators, sawmills, and subway systems. These motors can be used in many applications, and their range of applications is almost limitless.
Energy efficiency standards apply to all asynchronous AC electric motors. The IEC has implemented the IEC 60034-2-1:2014 energy efficiency standard, but many countries have their own national standards for electric motor efficiency. In the United States, NEMA, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, has set a minimum level for efficiency for industrial motors, known as IE2.
.png)
 English
English عربى
عربى
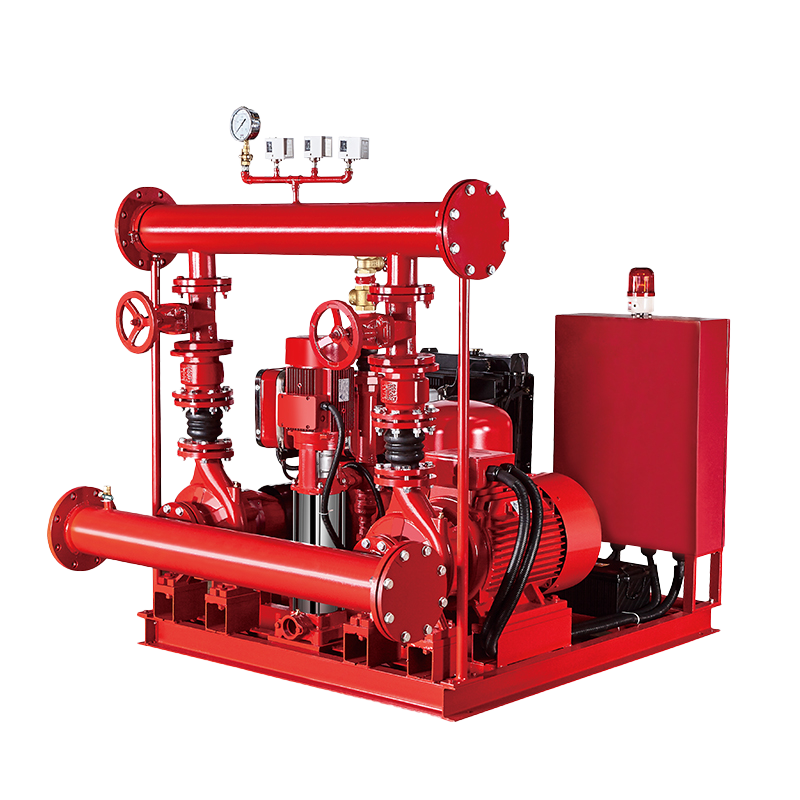 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System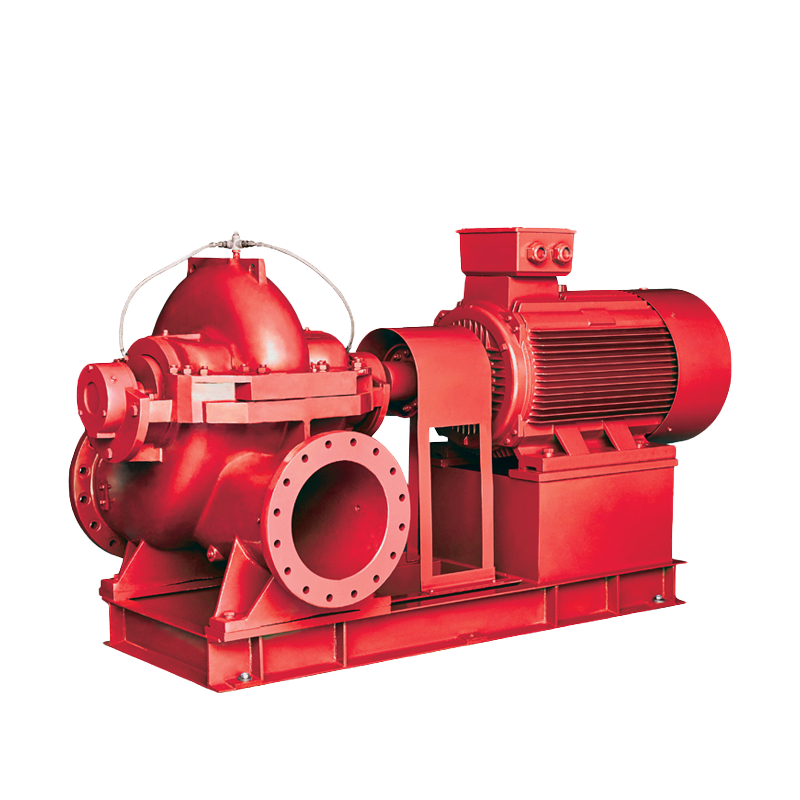 Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump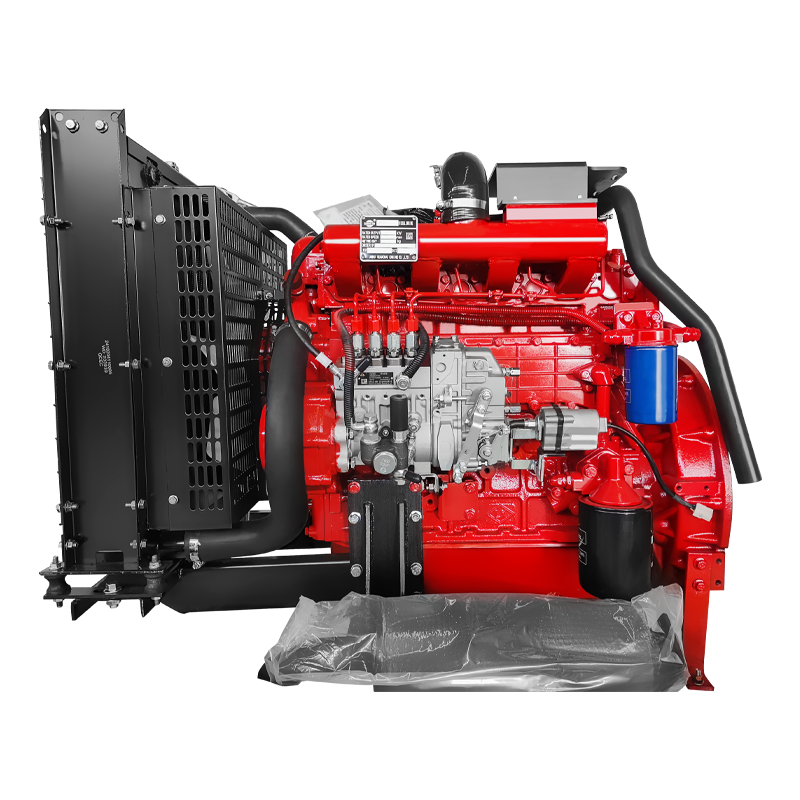 Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump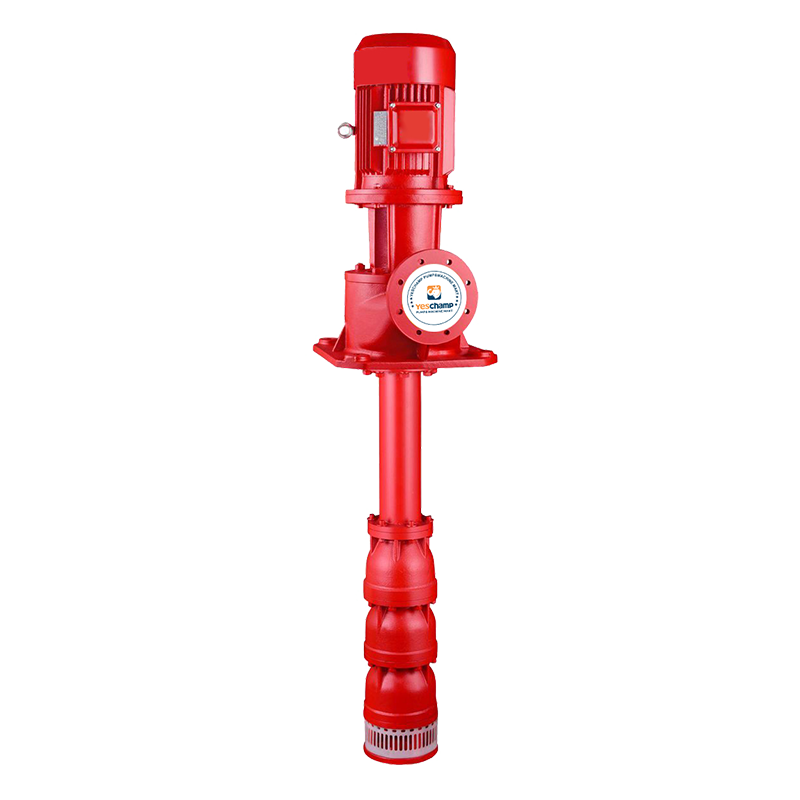 Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump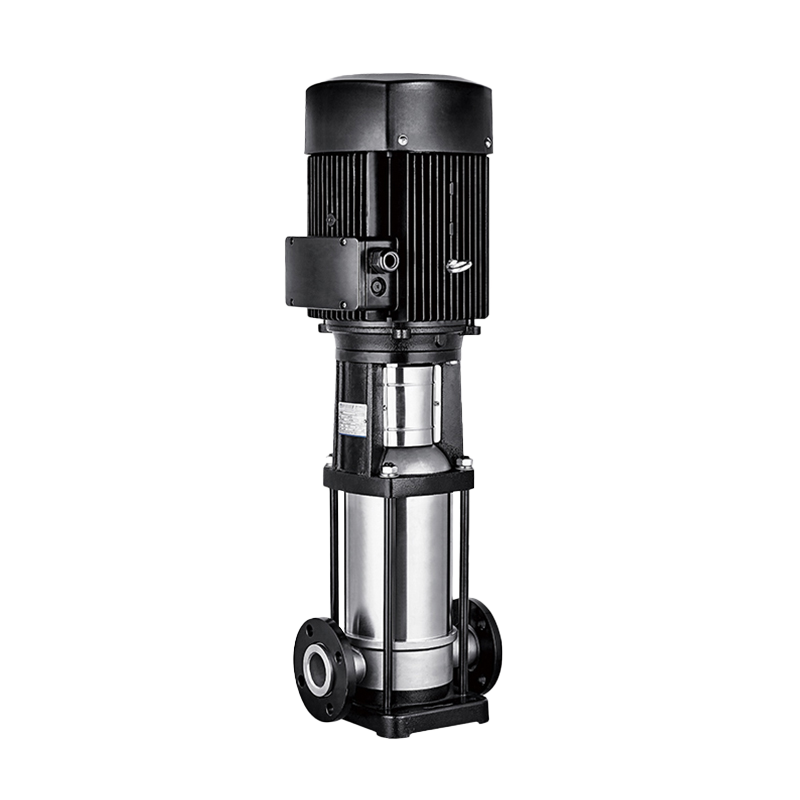 Multistage pump
Multistage pump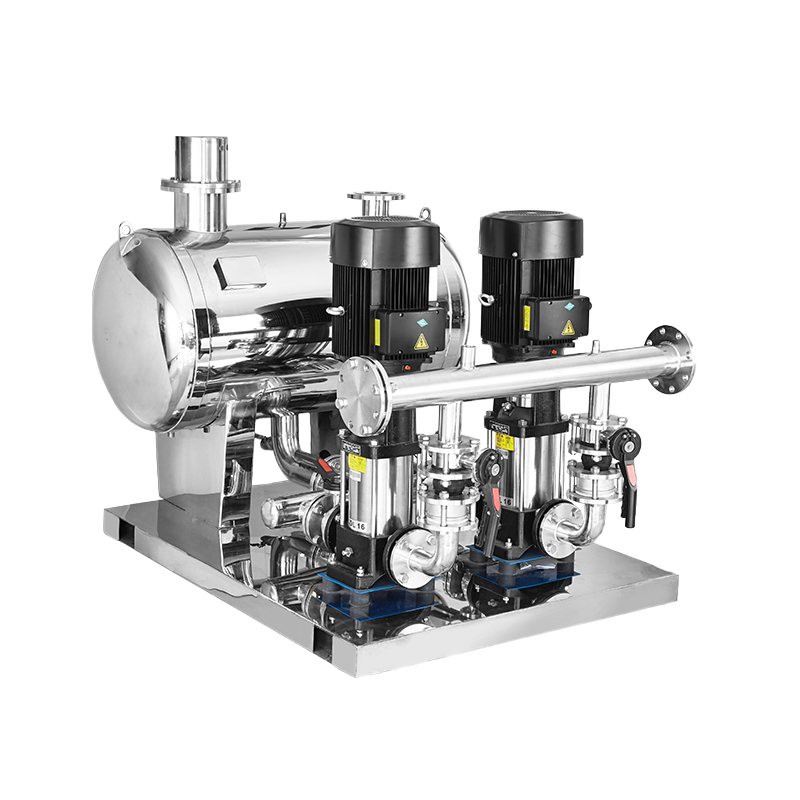 Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump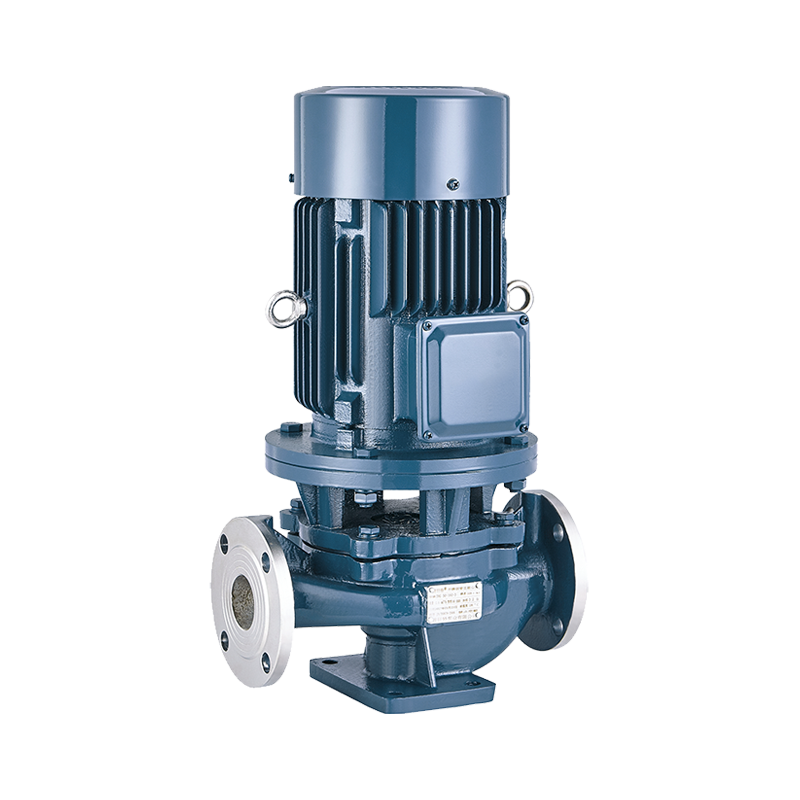 Inline Pump
Inline Pump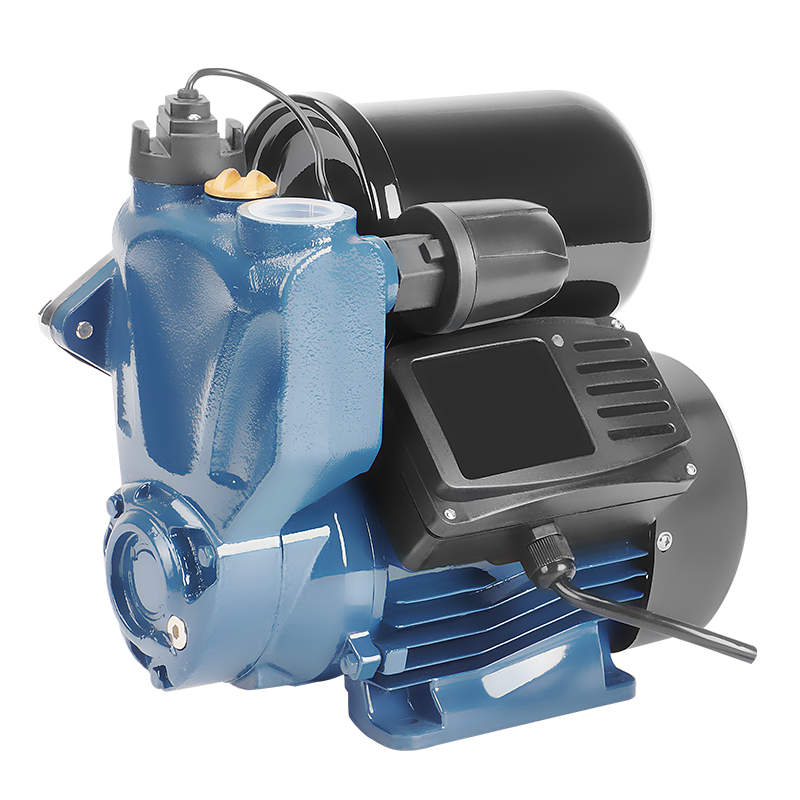 Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump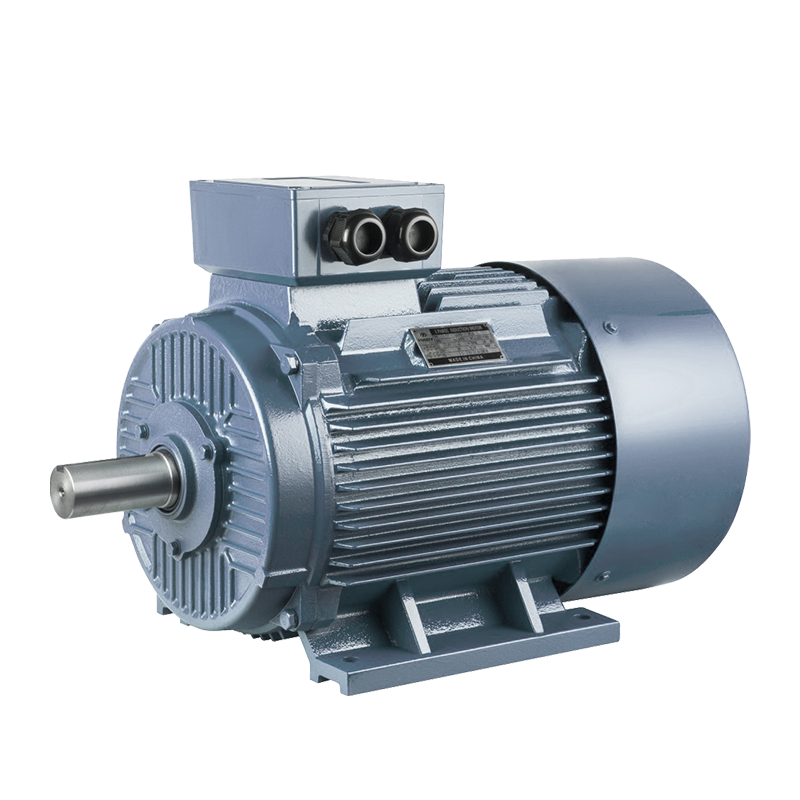 Electric Motor
Electric Motor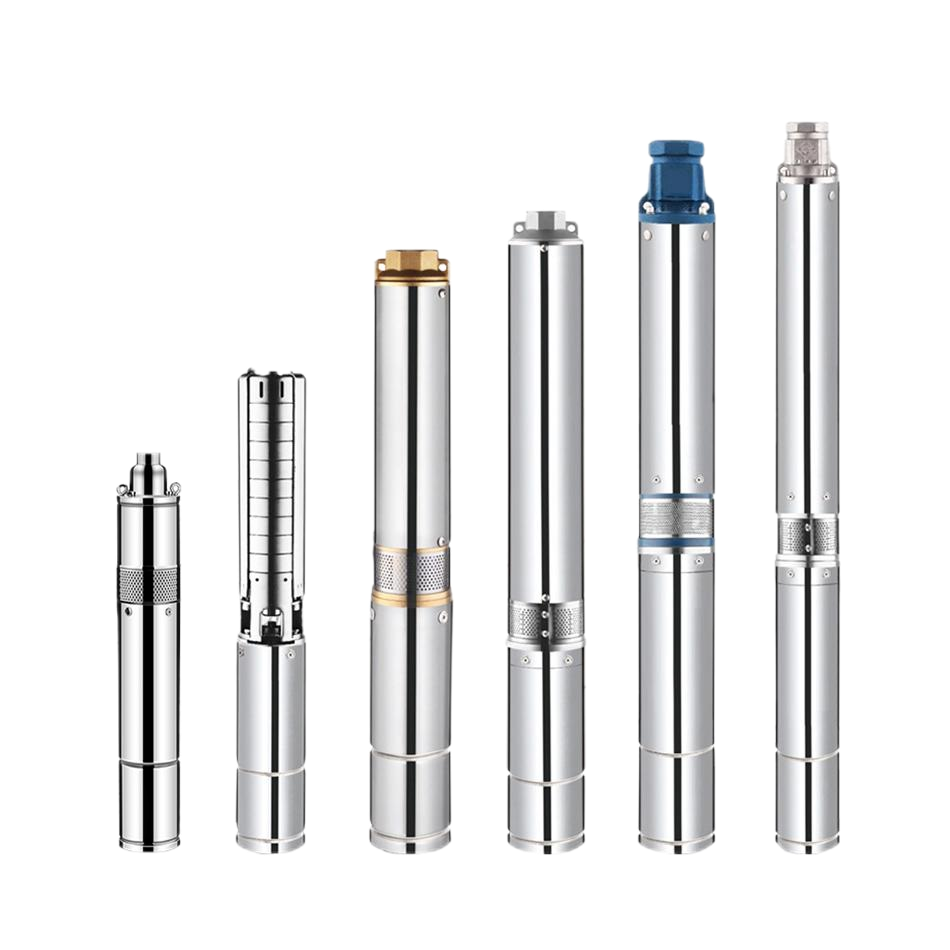 Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump







