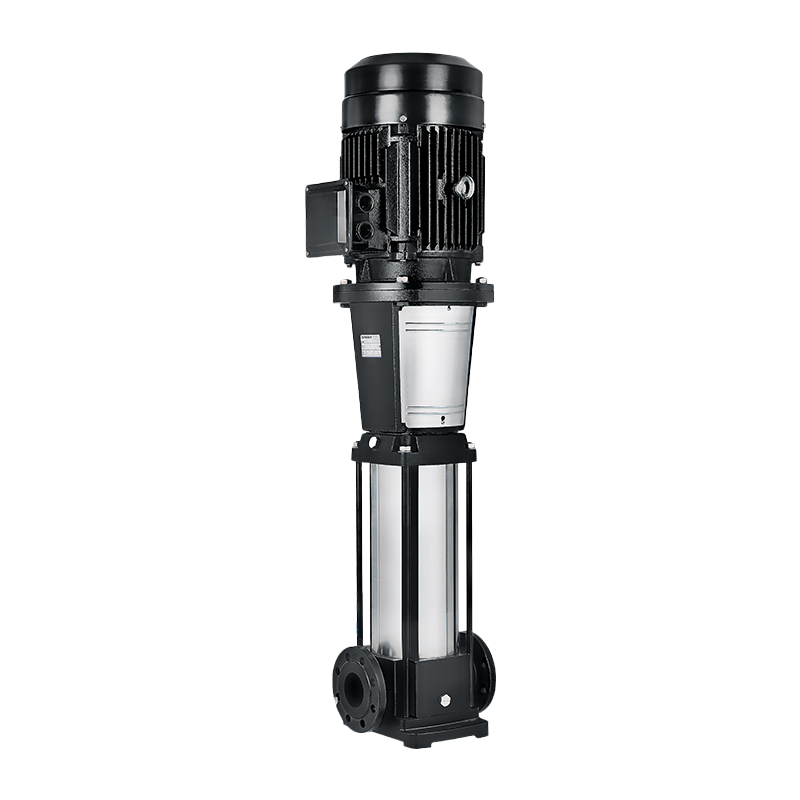
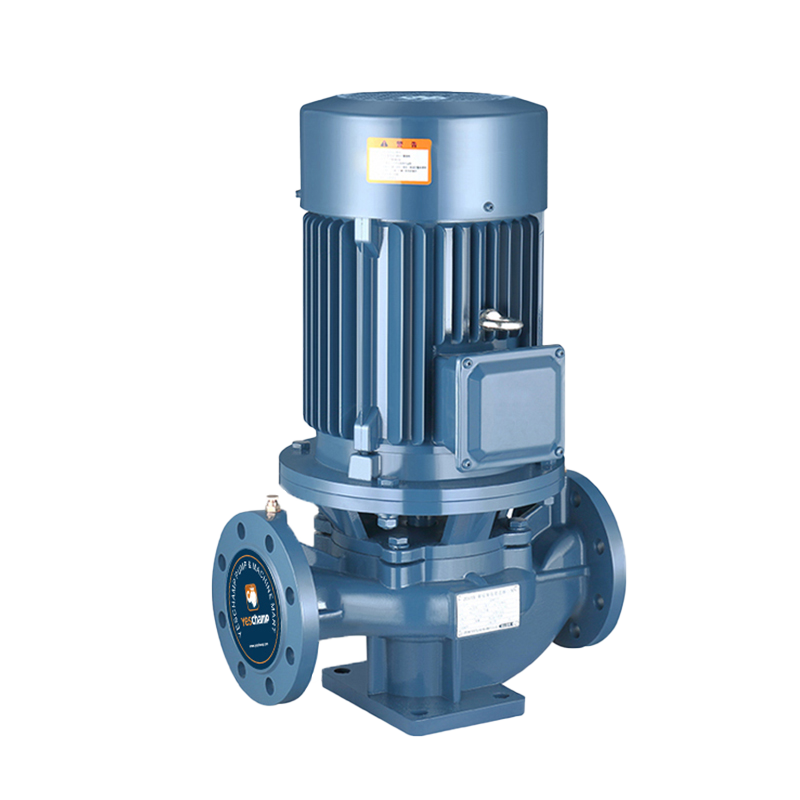
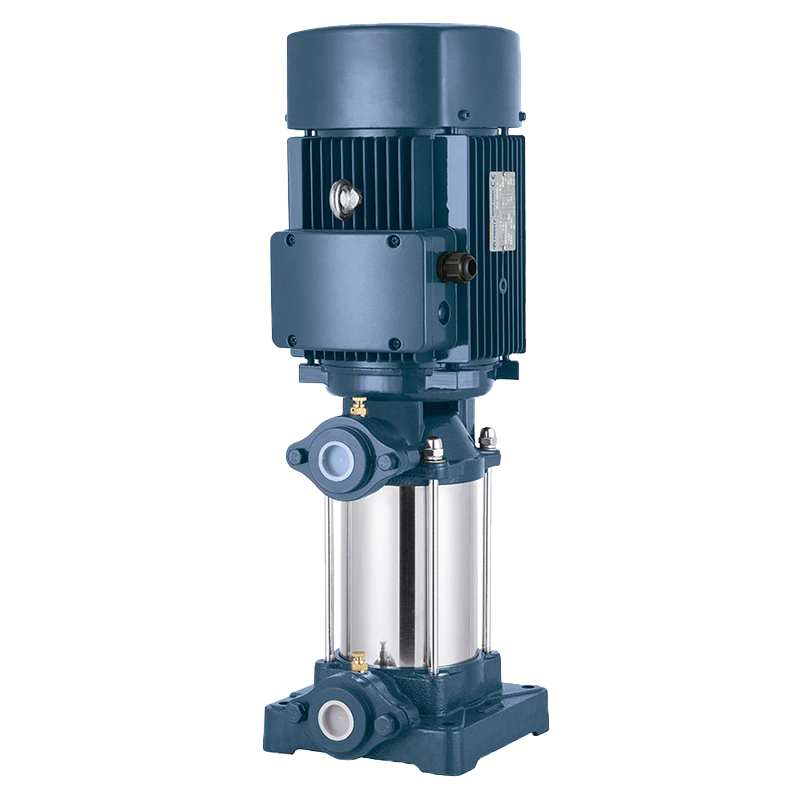
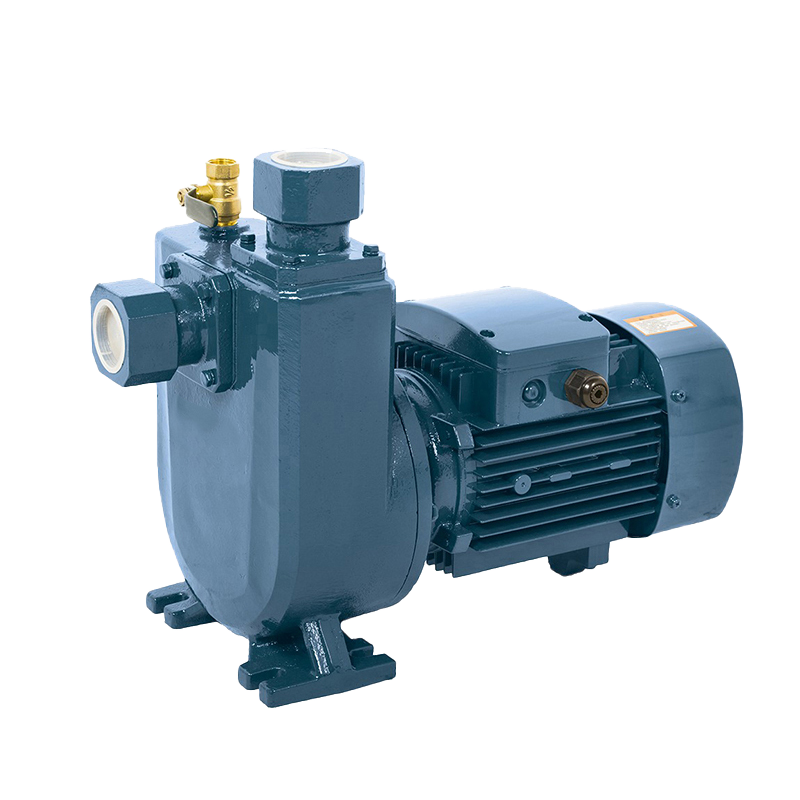
Vertical inline pumps are an ideal solution to your pumping needs. They are ideal for plumbing applications, as well as HVAC and computer cooling systems. The vertical design of the pump allows for easy maintenance of the shaft and mechanical seal. In addition, the pump is designed to fit seamlessly into piping systems.
A typical vertical inline pump is a centrifugal pump. It is driven by a direct-drive vertical electric motor. It does not require a baseplate, and it remains inline with suction and discharge connections. Depending on the type of pump, a spacer coupling or a close-coupled design is employed.
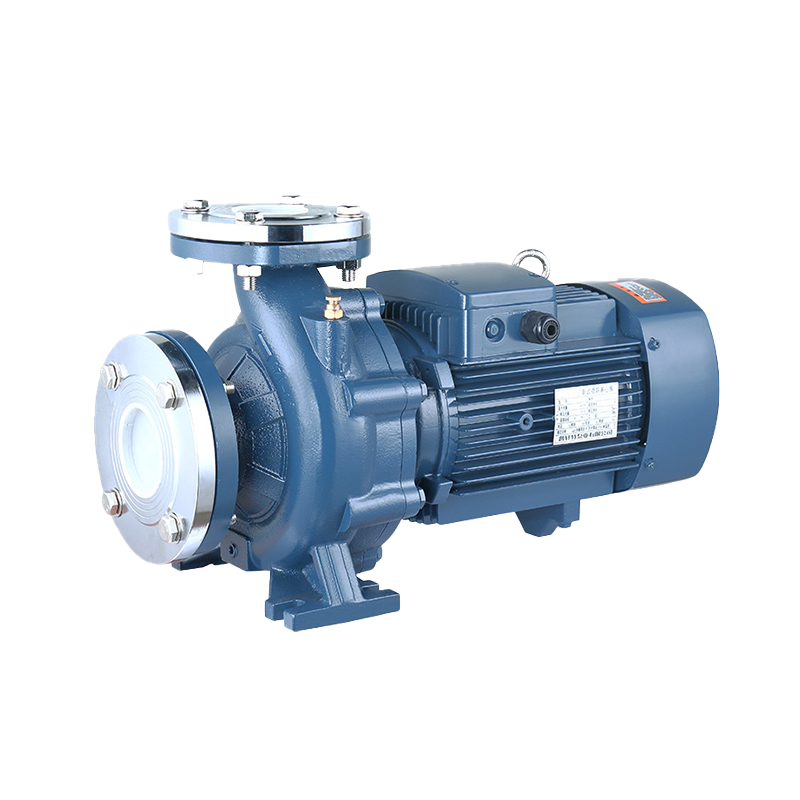
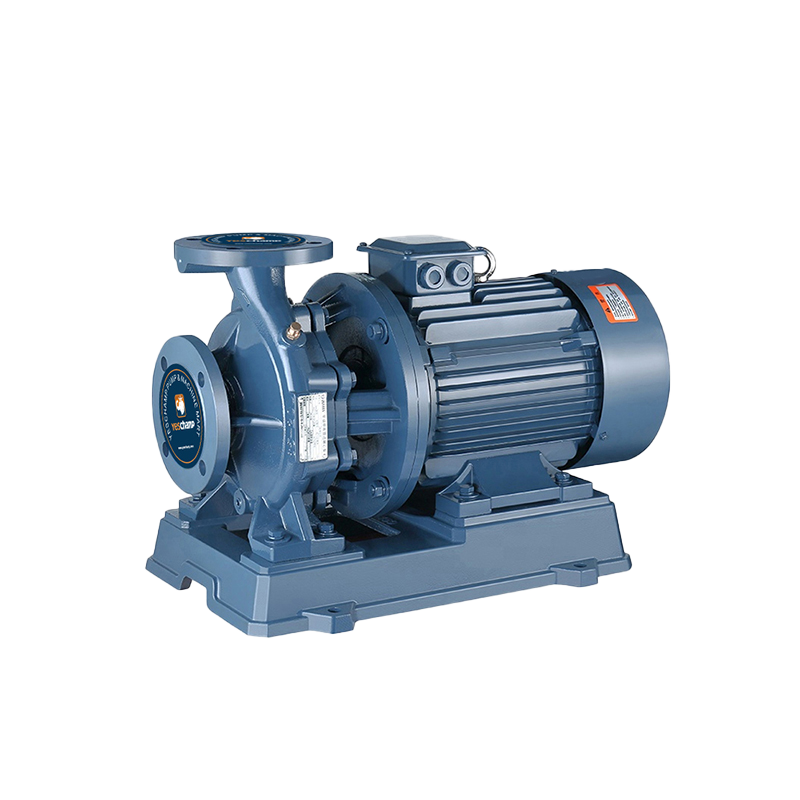
Centrifugal pumps are generally used in applications where a high center of gravity is required. The impeller is also a key component of the pump, and the centrifugal force causes the liquid to move radially outward. The tangential flow is then channeled into a diffusion system, which converts the high velocity to high pressure.
Pumps are designed to increase efficiency and reduce radial loads. These pumps are ideal for a variety of applications, including engine cooling and fire pumping. Several types of pumps are available. However, it is important to consider which one is most appropriate for your application. For example, a vertical turbine pump can be installed in high-temperature environments. On the other hand, a radial-flow vertical inline pump may not be suitable for high-pressure service.
The shaft of a centrifugal pump is usually lubricated by the fluid it is pumping. Some manufacturers use grease-lubricated bearings. Another common solution is to use hydrodynamic radial bearings in high-speed pumps. There are some flex-coupled VILs, but they are rarer than the other designs. Regardless of which type of pump you choose, be sure to check all the details. This will help to ensure the long-term durability and trouble-free operation of your pump.
Close-coupled vertical inline pumps have a longer path to the impeller than end-suction designs. The flange and nozzle load limits of a vertical pump are much higher than those of a horizontal pump of the same size. Therefore, it is vital to review the details and make sure that the bearings are in good condition.
Depending on the type of application, a pump can be a durable option for many vertical inline pumping applications. Generally, these pumps can be operated 24 hours a day. Because of this, they can be an ideal solution for applications where there is limited maintenance time. Unlike vertical end-suction pumps, a vertical inline close-coupled pump is self-aligned and does not require a baseplate. In addition, the suction and discharge connections are in line with the shaft. Nevertheless, this style of pump can cause additional problems.
Due to the tangential nature of the flow, the pump's exit pressure is generally at a high residual pressure. This allows the liquid to be pumped to a high vertical location, such as a tanker/terminal farm. When choosing a vertical inline pump, consult an experienced engineer for more information.

 English
English عربى
عربى
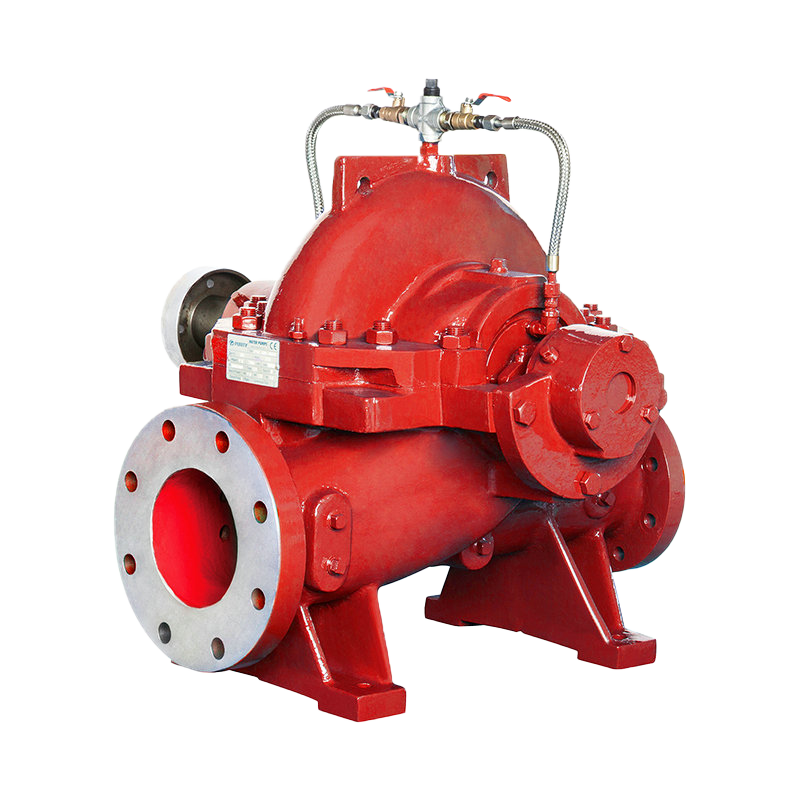
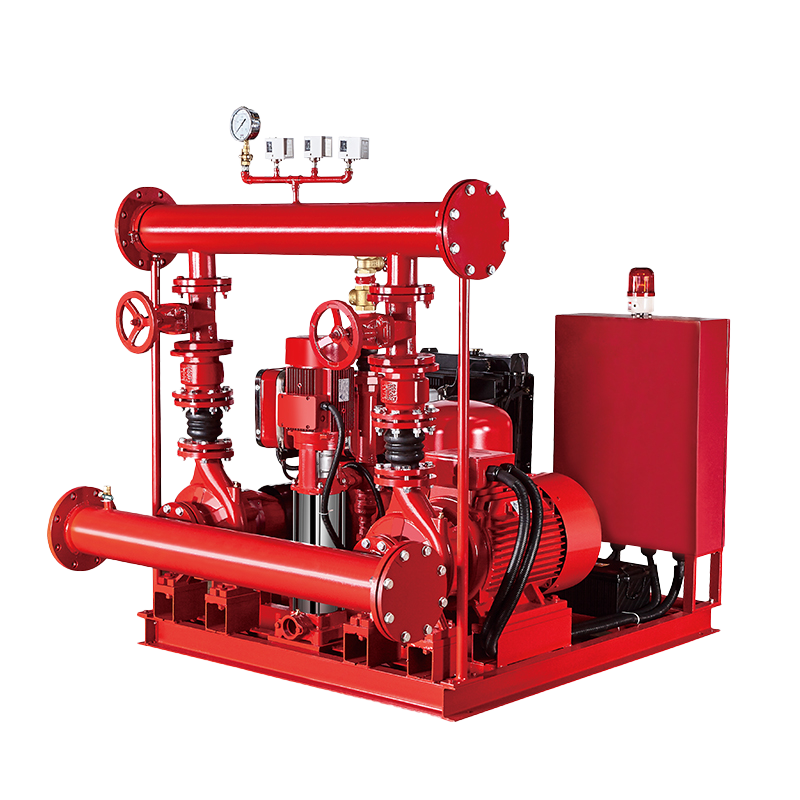 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System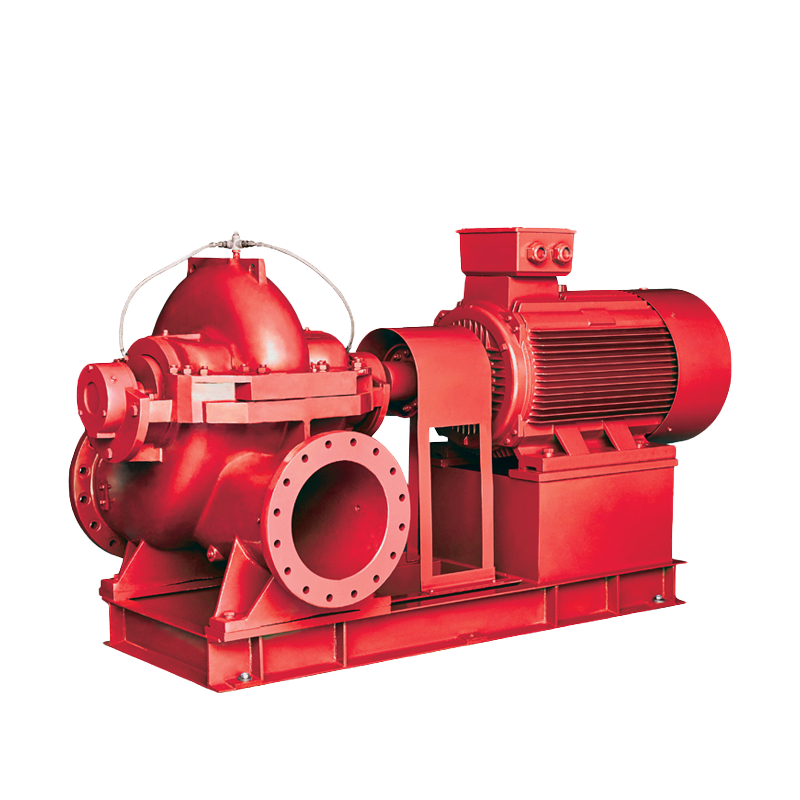 Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump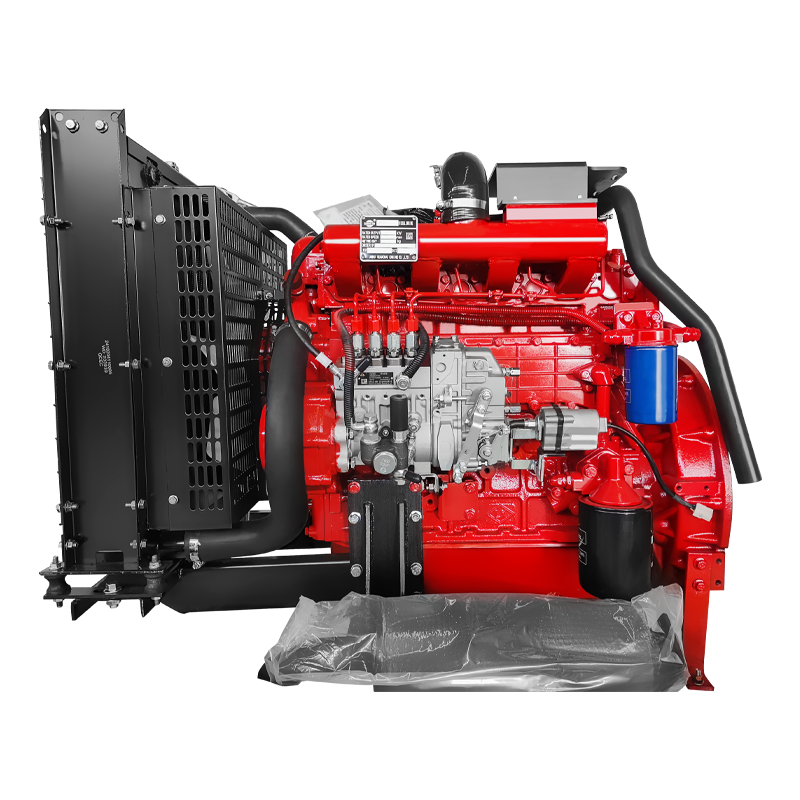 Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump Long Shaft Pump
Long Shaft Pump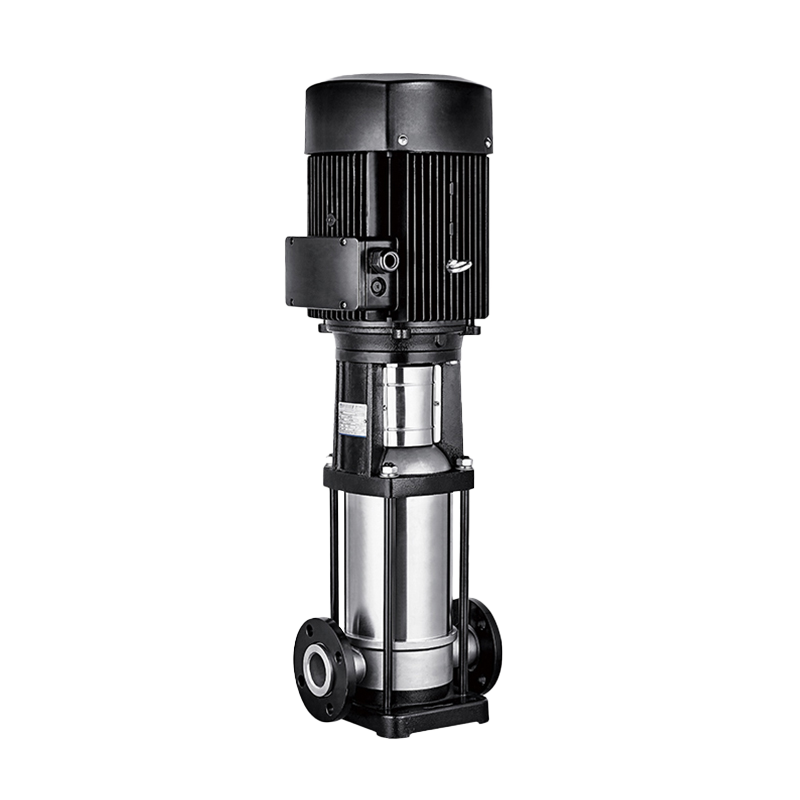 Multistage pump
Multistage pump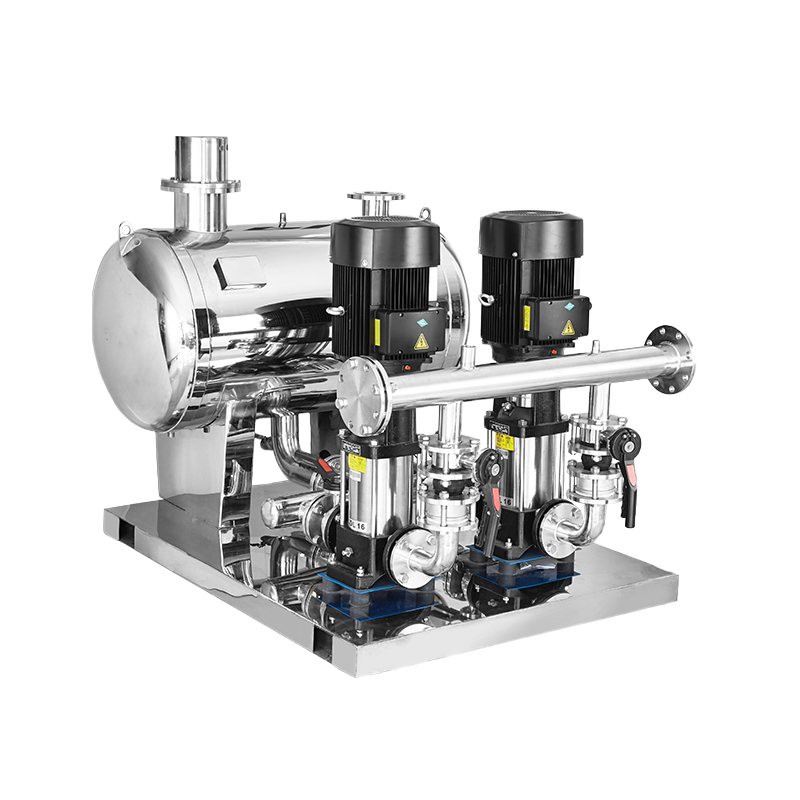 Water Supplier System
Water Supplier System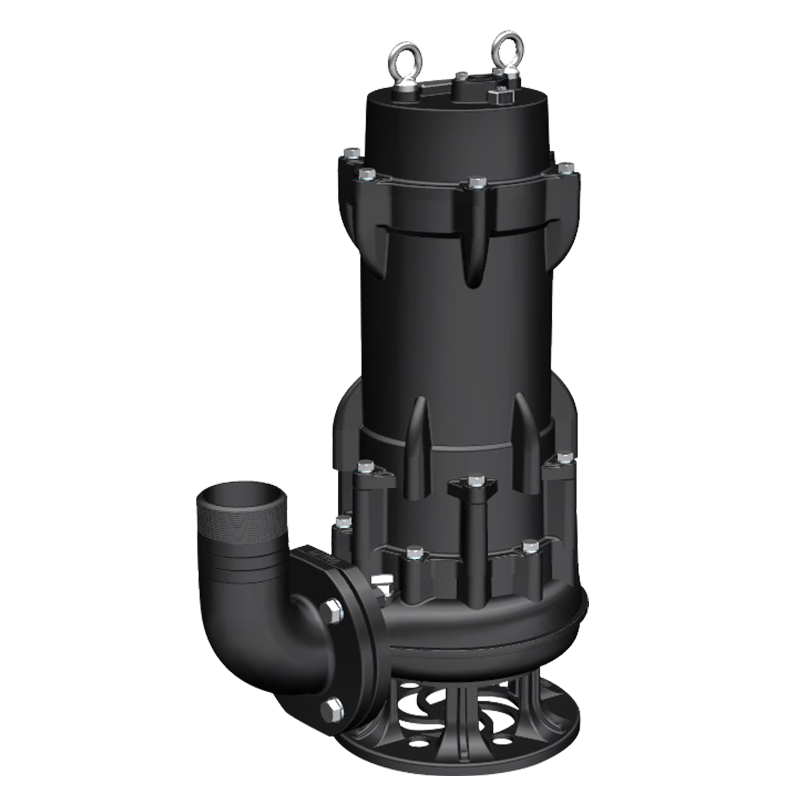 Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump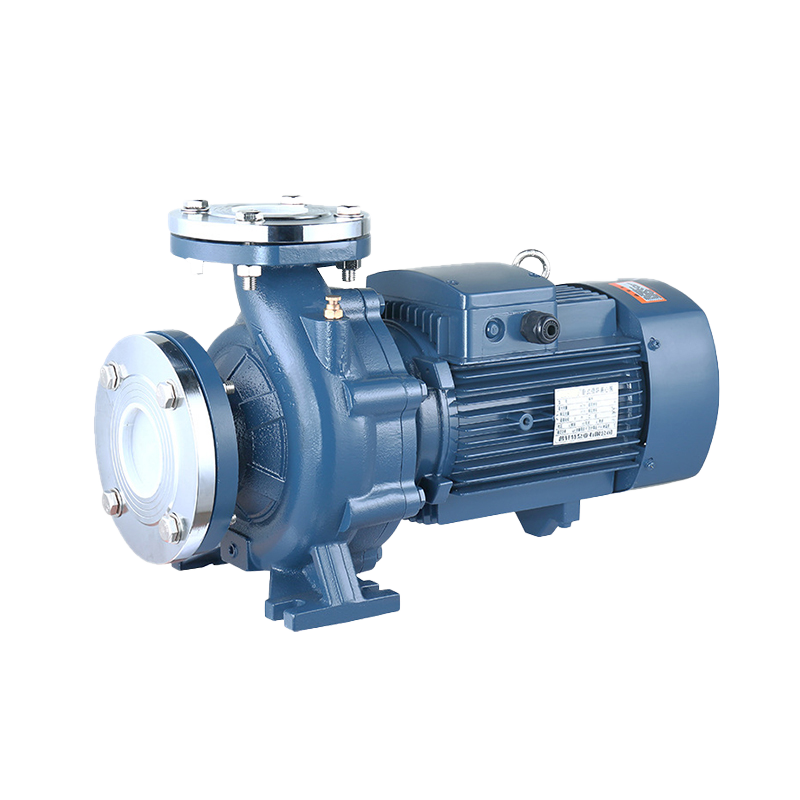 Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump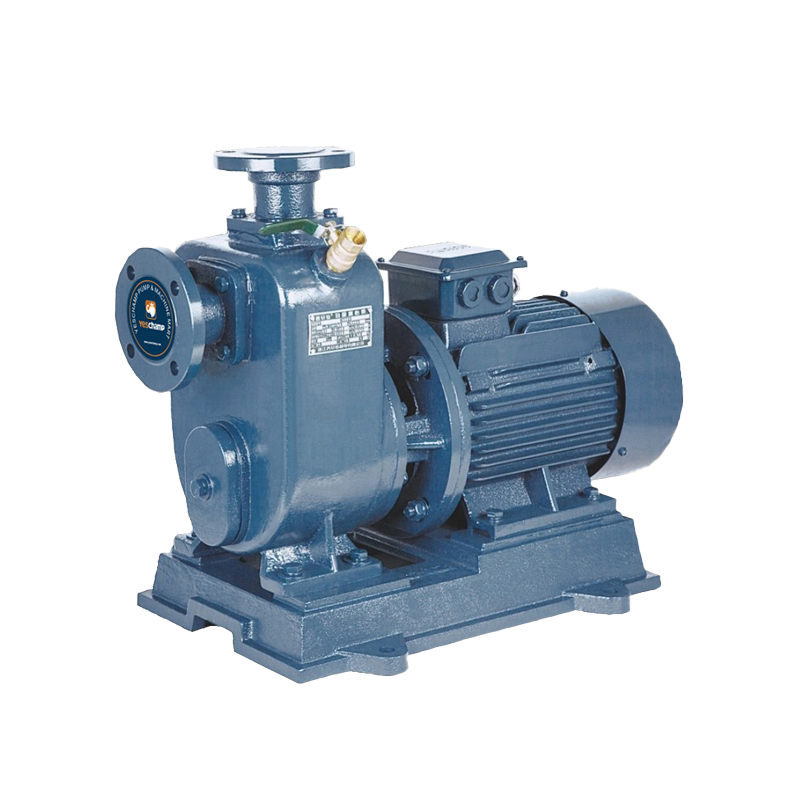 Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump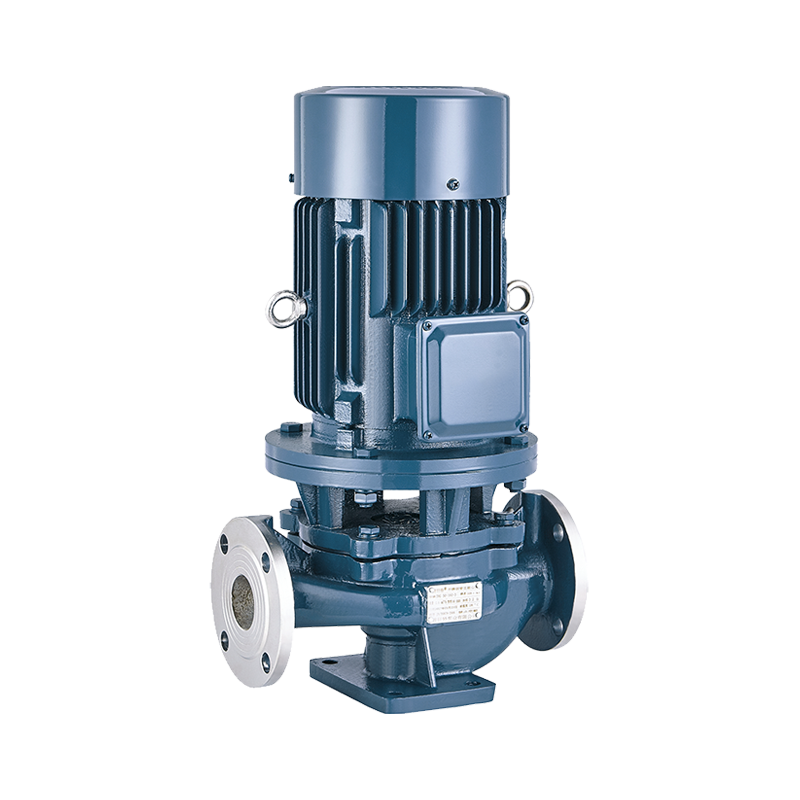 Inline Pump
Inline Pump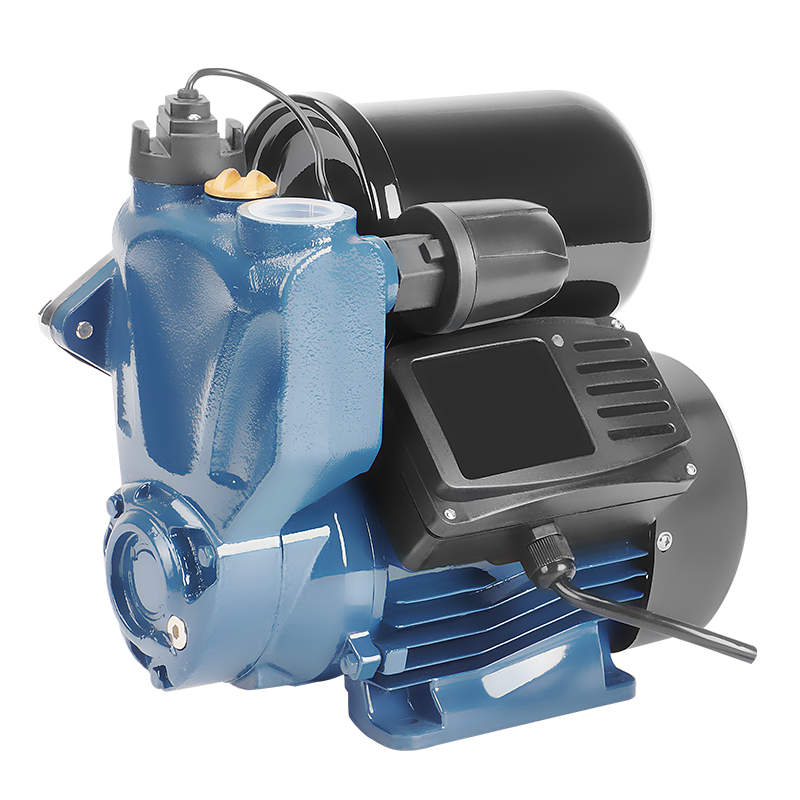 Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump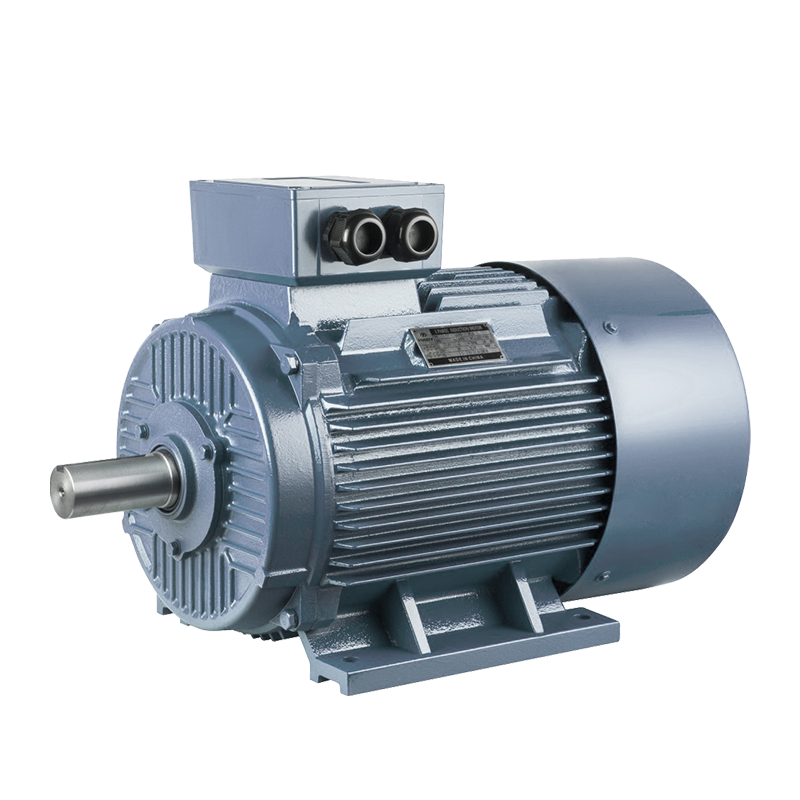 Electric Motor
Electric Motor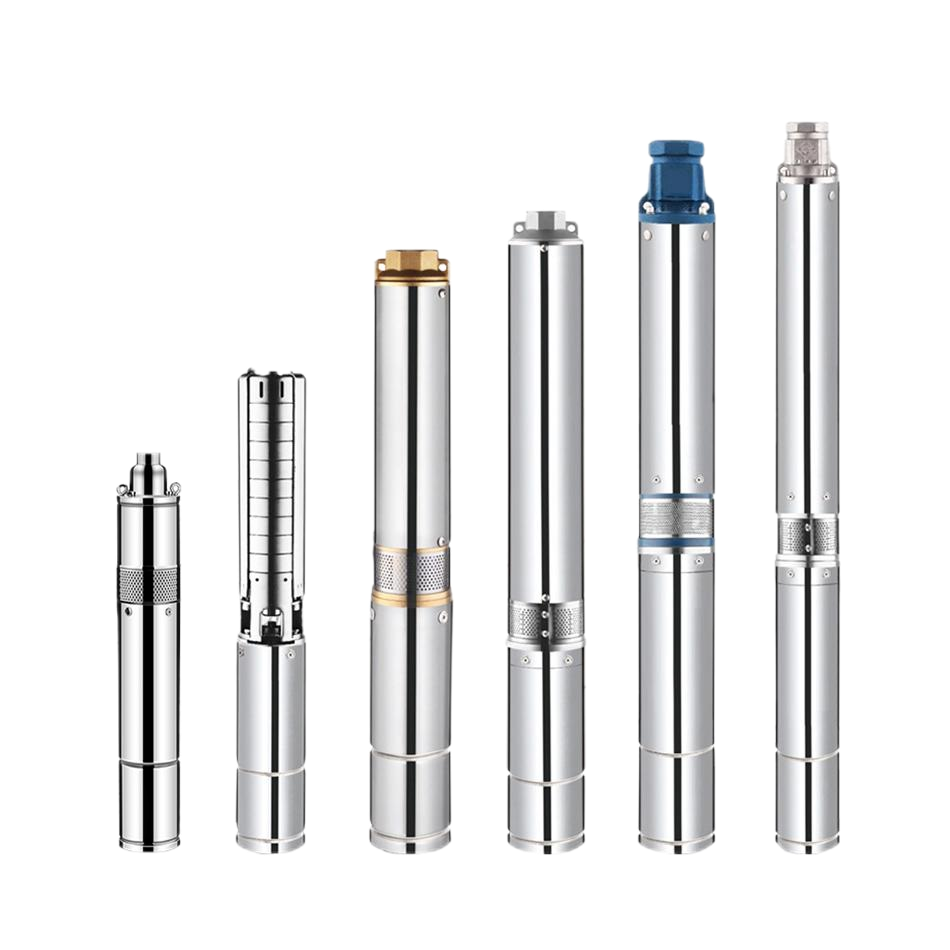 Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump