"Efficient Fluid Transport: Unleashing the Power of Pipeline Pumps"
Introduction:
Pipeline pumps play a crucial role in efficiently transporting fluids across vast distances, from water and oil to gas and chemicals. In this article, we will explore the significance, functionality, and advantages of pipeline pumps, shedding light on their essential role in fluid transportation.
The Significance of Pipeline Pumps:
Pipeline pumps serve as the heart of fluid transportation systems, enabling the efficient movement of liquids or gases over long distances. They are essential in industries such as oil and gas, water supply, wastewater management, and chemical processing.
How Pipeline Pumps Work:
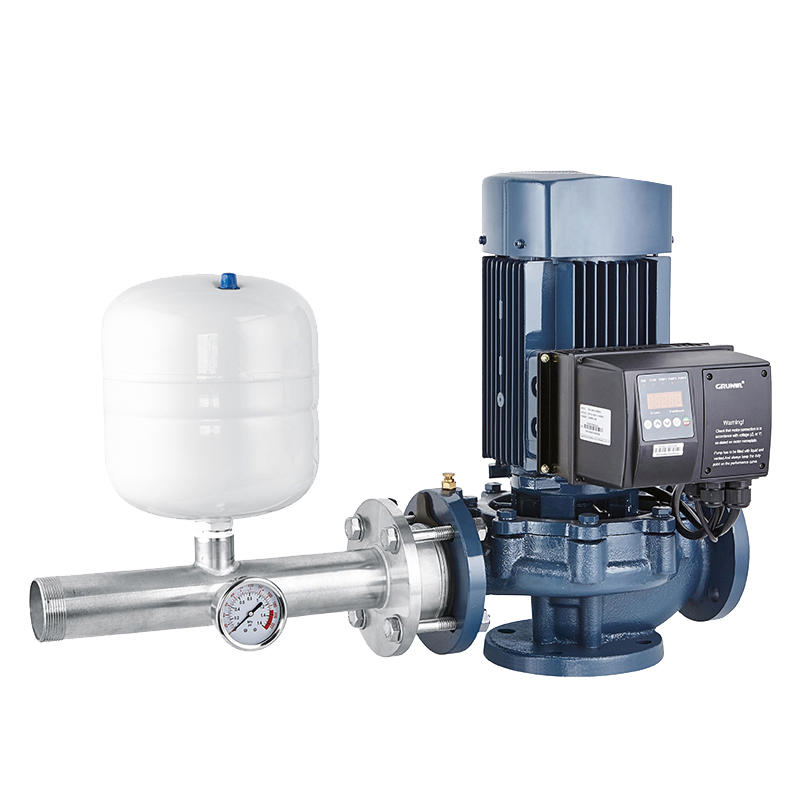
Pipeline pumps operate by creating the necessary pressure to propel fluids through pipelines. They draw in the fluid at the inlet, increase its pressure, and then discharge it at a higher pressure at the outlet. This process ensures a continuous flow of the transported fluid with minimal energy loss.
Types of Pipeline Pumps:
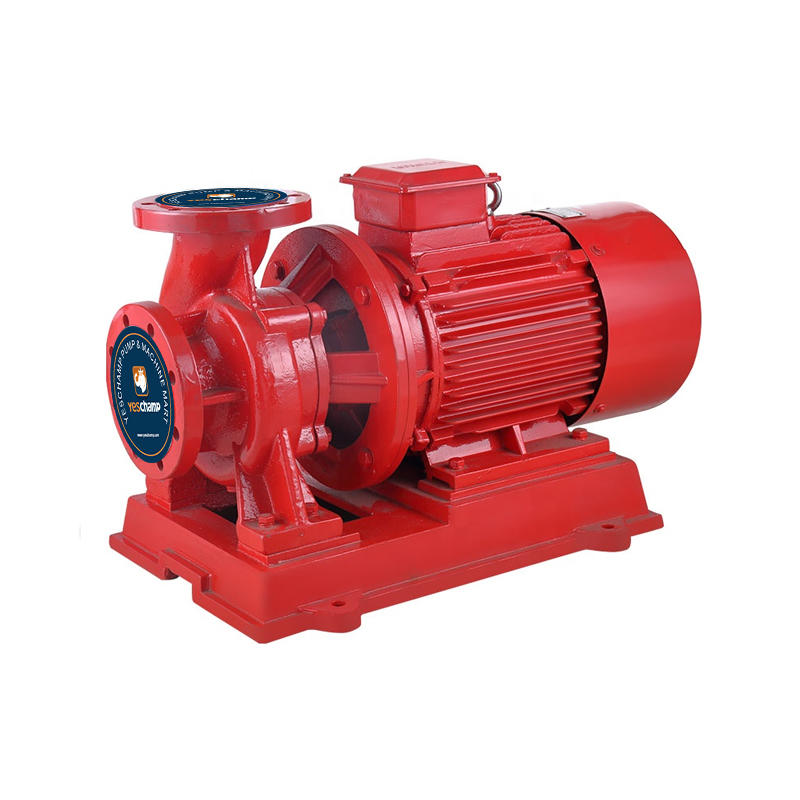
a. Centrifugal Pumps: Widely used in pipeline systems, centrifugal pumps rely on centrifugal force to increase fluid pressure. They are known for their high flow rates, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
b. Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps use reciprocating or rotary mechanisms to move fluid in fixed volumes, making them suitable for applications requiring precise control or handling viscous fluids.
Advantages of Pipeline Pumps:
a. Efficient Fluid Transportation: Pipeline pumps minimize energy losses and ensure a continuous flow, reducing the need for intermediate storage or additional pumping stations.
b. Cost Savings: By efficiently transporting fluids over long distances, pipeline pumps reduce operational costs associated with transportation, storage, and handling.
c. Environmental Benefits: Pipeline pumps help reduce the carbon footprint by minimizing the use of transport vehicles and decreasing the risk of spills or leaks associated with alternative transportation methods.
d. Versatility: Pipeline pumps can handle various types of fluids, including water, oil, gas, and chemicals, making them adaptable for a wide range of industries and applications.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations:
Regular maintenance, including inspections, lubrication, and proper alignment, is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of pipeline pumps. Additionally, following safety protocols and implementing fail-safe mechanisms is essential to mitigate potential risks associated with fluid transportation.
Conclusion:
Pipeline pumps are indispensable for efficient fluid transportation, enabling the movement of liquids and gases over long distances with minimal energy loss. By harnessing the power of pipeline pumps, industries can achieve cost savings, environmental benefits, and reliable fluid transport. Embracing these advanced pumping solutions contributes to improved efficiency, sustainability, and effectiveness in various sectors.
 English
English عربى
عربى
 Fire Pump and System
Fire Pump and System Split Case Pump
Split Case Pump Engine and Pump
Engine and Pump Long Shaft Pump
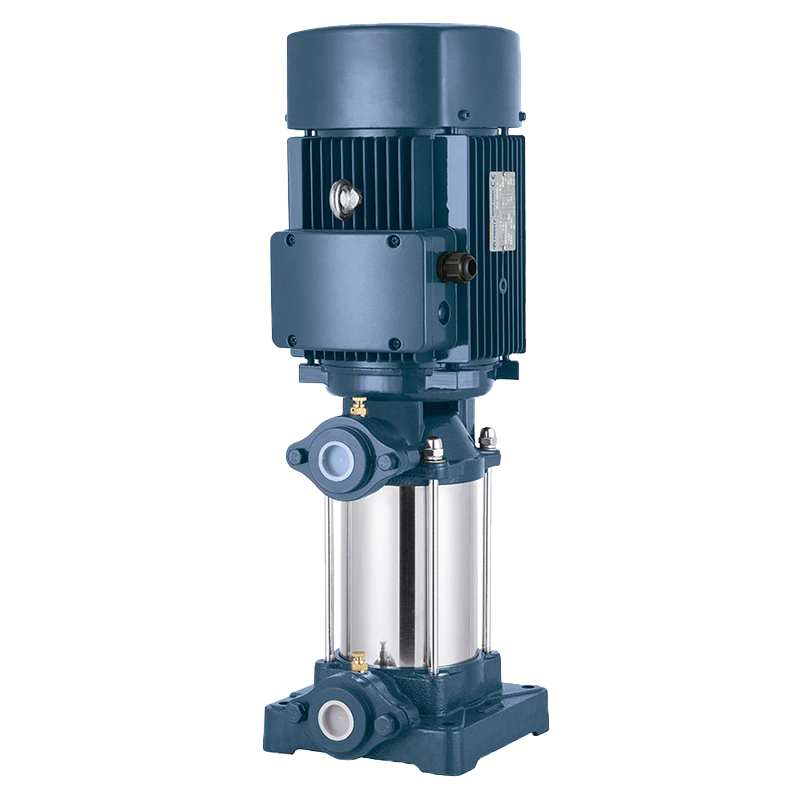
Long Shaft Pump Multistage pump
Multistage pump Water Supplier System
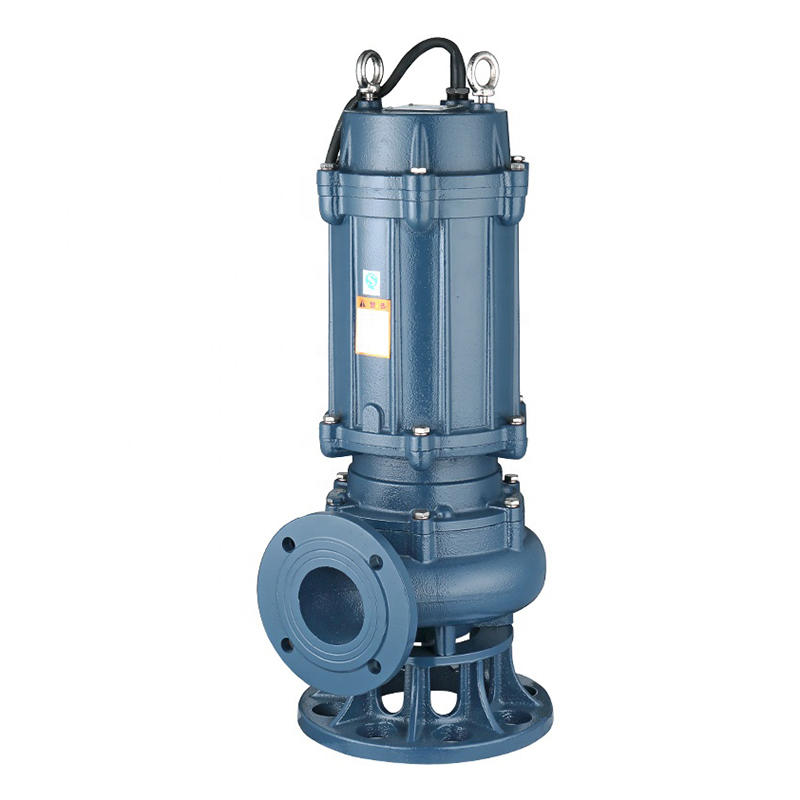
Water Supplier System Sewage Pump
Sewage Pump Industrial Pump
Industrial Pump Self-Priming Pump
Self-Priming Pump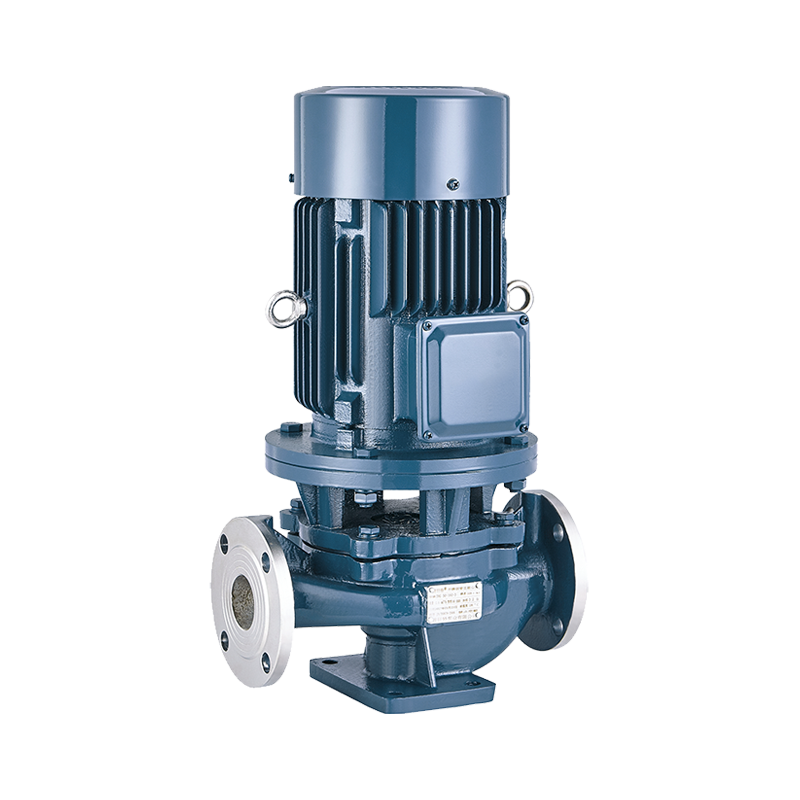 Inline Pump
Inline Pump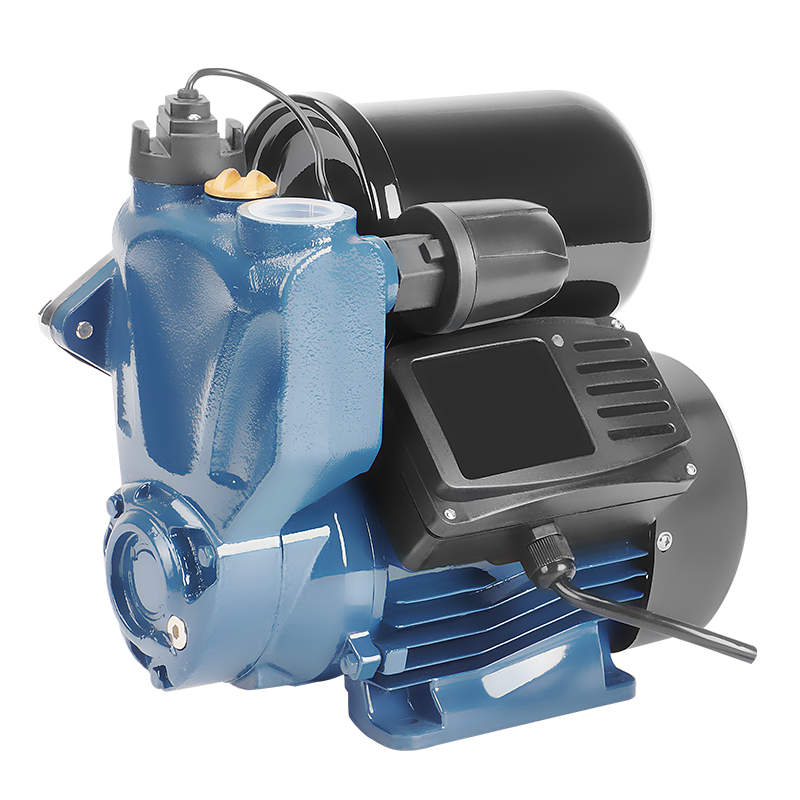 Domestic Pump
Domestic Pump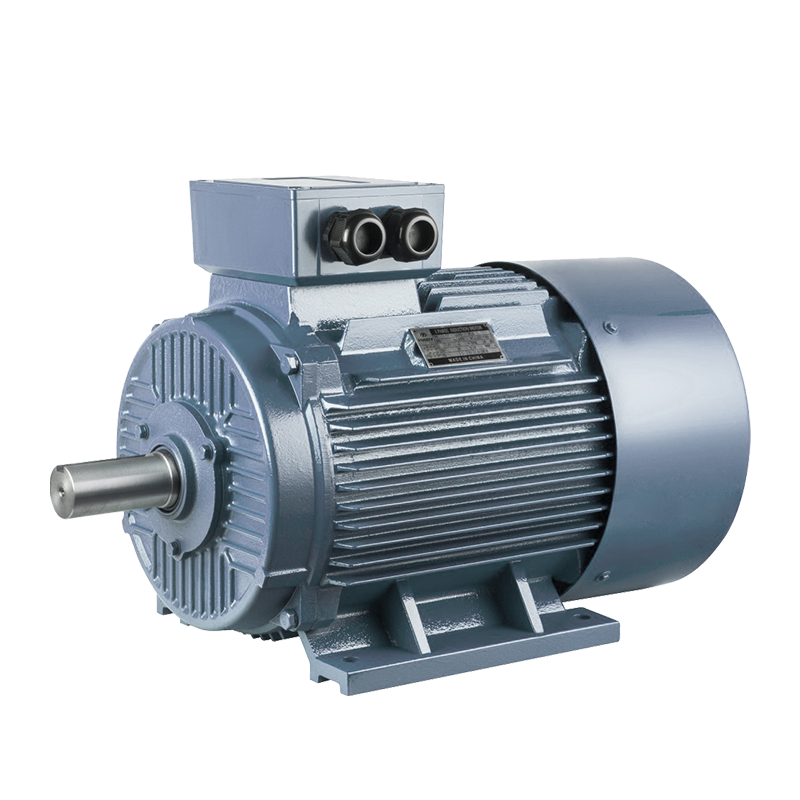 Electric Motor
Electric Motor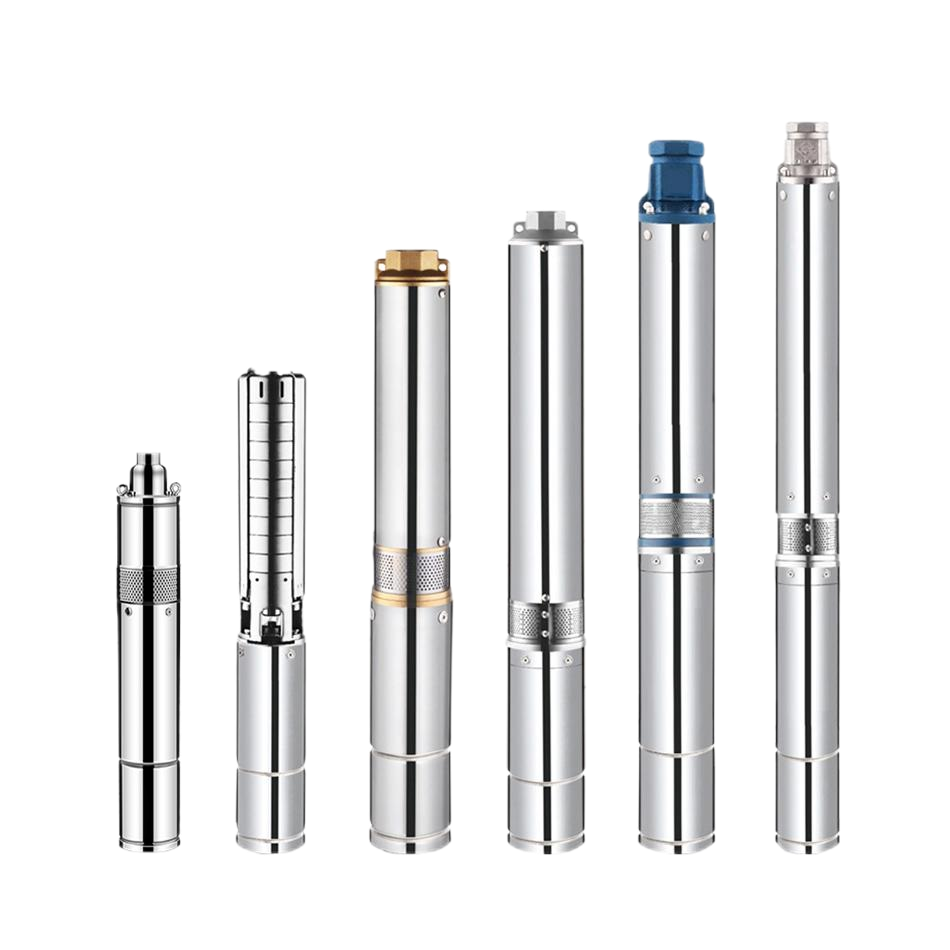 Borehole Pump
Borehole Pump